Sleep Apnea Sleep Positions: Best & Worst

There’s no doubt about the importance of sleep, but what can you do when your sleep is constantly interrupted? Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can significantly impact your quality of sleep, leading to daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and other health issues. Your sleep position is one factor that can influence the severity of sleep apnea. Certain sleeping positions can either worsen or alleviate the symptoms of sleep apnea.
Understanding the best and worst sleeping positions for sleep apnea is crucial for alleviating its symptoms and improving your overall sleep quality. In this article, we’ll explore the best sleeping positions for sleep apnea and those that are discouraged, offering insights into how simple changes in sleeping habits can positively impact your well-being.
- What Is Sleep Apnea?
- What Is the Best Sleeping Position for Sleep Apnea?
- What Is the Worst Sleeping Position for Sleep Apnea?
- How Can You Alleviate Sleep Apnea Symptoms?
- Key Takeaways: Best Sleeping Positions for Sleep Apnea
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by recurrent disruptions in breathing during sleep. These interruptions, known as apneas, can be partial or complete and may last for a few seconds to minutes. The most common form of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where the muscles in the throat relax excessively, leading to a partial or complete blockage of the upper airway.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is another form caused by the brain’s failure to send signals to the muscles that control breathing.
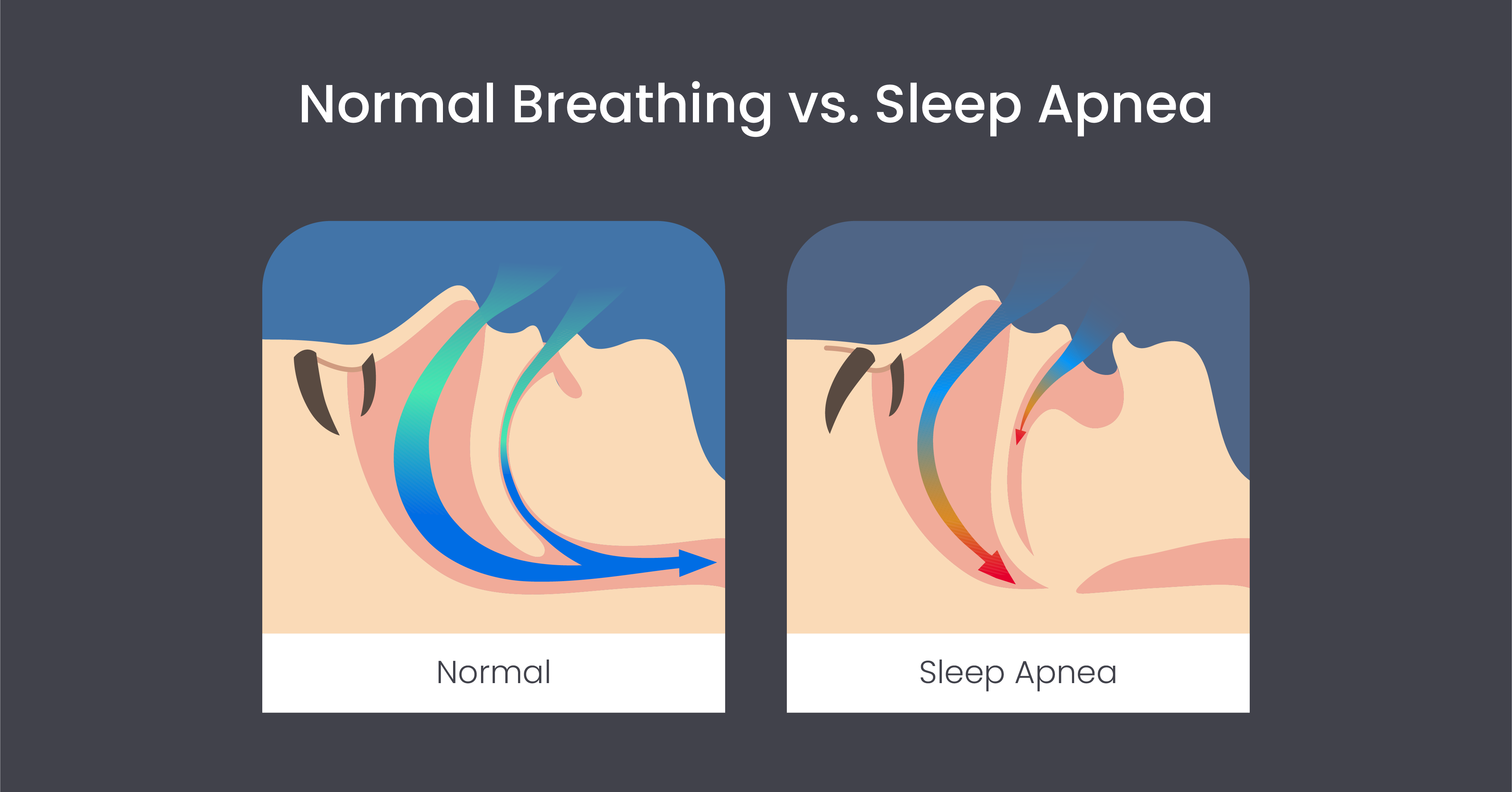
The impact of sleep apnea on sleep is profound and can lead to a range of consequences, such as waking up in the middle of the night. This fragmented and unrestful sleep experience can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue, and in some cases, you may find yourself waking up with headaches.
Sleep apnea can also affect your bed partner as well, as loud and persistent snoring is a common symptom. Additionally, the chronic sleep disruptions associated with sleep apnea may contribute to insomnia, making it even more challenging to get restorative sleep.
The cumulative effects of sleep apnea on overall health are significant, including the risk of cardiovascular issues, metabolic disorders, and impaired cognitive function.
What Is the Best Sleeping Position for Sleep Apnea?
Managing sleep apnea involves medical help and lifestyle adjustments, including changing your sleep position if necessary. While changing your sleep position may not be the cure to sleep apnea, it can help reduce some of the disruptions to your sleep, helping you get more restorative rest at night. Among various sleep postures, side and stomach sleeping have been identified as particularly beneficial for those with sleep apnea.
Side Sleeping
Side sleeping is often recommended as the best sleep position for sleep apnea due to its potential to alleviate symptoms and improve breathing patterns. When sleeping on your side, your airway is generally more open and less prone to collapse compared to back sleeping. This can be especially beneficial for those with OSA.
Among the different side sleeping positions, the fetal position, where the knees are drawn toward the chest, is a popular choice. This position helps open the airways and can reduce the risk of snoring and apneas. The log position and hugger position are also variations that can promote better airflow.
There’s also some debate about whether sleeping on the right or left side is better. Some research suggests that sleeping on the left side may be better for those with sleep apnea because it can help reduce acid reflux symptoms, which can be beneficial for those with both sleep apnea and acid reflux.
Stomach Sleeping
Another sleep apnea sleeping position that may work for you is stomach sleeping. Stomach sleeping is a position that doesn’t typically obstruct your airway, making it a potential choice for those with sleep apnea. When sleeping on your stomach, your tongue is less likely to fall backward into the throat, reducing the likelihood of airway blockages. However, stomach sleeping isn’t right for everyone.
While it may help prevent apneas, it comes with its own set of challenges. Sleeping in this position can lead to unnatural alignment of the neck and spine, potentially causing back and neck pain over time. To mitigate these issues, sleeping with pillows can help you maintain a more neutral alignment for your head and neck.
Stomach sleeping might not be the best option for everyone, but with proper pillow support, it can be a good option for those with sleep apnea symptoms while avoiding the potential drawbacks associated with other sleeping positions.
What Is the Worst Sleeping Position for Sleep Apnea?
While choosing the best sleep position for sleep apnea can improve your symptoms, not all sleep positions will work for you. Certain sleep positions can worsen symptoms and contribute to more severe breathing disruptions. One of the positions often discouraged for those with sleep apnea is back sleeping.
Back Sleeping
Sleeping on your back, also known as the supine position, is often considered the worst position to sleep with sleep apnea. When you lie on your back, gravity tends to pull the tongue and soft tissues of the throat backward, causing the airway to narrow. This narrowing can lead to an increased likelihood of snoring and, more significantly, contribute to OSA.
In OSA, the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, partially or completely blocking the airway. When combined with the effects of gravity in the supine position, this relaxation can become more pronounced, increasing the risk of airflow obstruction and interrupted breathing.
Those with positional sleep apnea may find that their symptoms worsen when sleeping on their backs, and making adjustments to sleep in a different position, such as on the side, can help alleviate some of these issues. Overall, avoiding back sleeping and exploring other sleeping positions may contribute to better sleep quality and health for those managing sleep apnea.
How Can You Alleviate Sleep Apnea Symptoms?
Alleviating sleep apnea involves a comprehensive approach that goes beyond selecting the right sleeping position. While side sleeping is often recommended to alleviate symptoms, there are additional measures you can take to improve your sleep quality and reduce the impact of sleep apnea, such as:
- Invest in the right mattress: Choosing the right mattress is crucial for individuals with sleep apnea. Opting for a memory foam or hybrid mattress that provides adequate support for the spine and distributes body weight evenly can enhance overall comfort. Medium-firm mattresses are often recommended, as they offer a balance of support and cushioning, helping to prevent discomfort and promote better sleep postures. If you don’t want to invest in a new mattress, you can try a mattress topper for improved support.
- Use supportive pillows: Supportive pillows can also help maintain proper head and neck alignment. Pillows that provide adequate support can keep the airways open and reduce the risk of snoring and breathing disruptions. Specialized pillows may also offer additional benefits.
- Establish a sleep routine: Creating a consistent sleep routine helps regulate the body’s internal clock, promoting a more predictable sleep-wake cycle. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends, reinforces your body’s natural circadian rhythm. This can improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of nighttime awakenings associated with sleep apnea.
- Avoid alcohol before bed: Alcohol is a muscle relaxant and relaxes the muscles in the throat. Consuming alcohol before bedtime can lead to increased relaxation of these muscles, contributing to airway obstruction and worsening sleep apnea symptoms. Limiting or avoiding alcohol intake in the hours leading up to sleep can be beneficial.
- Manage allergies: Nighttime allergies can worsen nasal congestion, making breathing more difficult for those with sleep apnea. Taking steps to manage allergies, such as using air purifiers, keeping living spaces clean, and using allergy-friendly bedding, can help reduce congestion and improve overall respiratory function during sleep.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can lessen the severity of sleep apnea symptoms. Losing weight is often recommended as part of a complete treatment plan.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration helps prevent mucus buildup in the airways, potentially reducing the risk of breathing difficulties during sleep.
- Consult a healthcare professional: Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is essential for a thorough assessment of sleep apnea and the development of an appropriate treatment plan. Healthcare providers can conduct sleep studies, recommend specialized interventions such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, and provide personal advice based on individual health needs.
Key Takeaways: Best Sleeping Positions for Sleep Apnea
Choosing the right sleeping position is crucial for those dealing with sleep apnea. Side sleeping is often recommended for its potential to alleviate symptoms and improve breathing during sleep. Stomach sleeping is also a good option, but it comes with its own considerations. On the other hand, back sleeping is generally discouraged as it can lead to increased snoring and worsen symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea.
In addition to adopting a good sleep position for sleep apnea, investing in the right sleep accessories can further improve your sleep quality. Layla Sleep offers a range of products designed to support a comfortable and restful night’s sleep. Browse our selection of memory foam mattresses, pillows, bedding, and more.






