While many people occasionally experience anxiety about sleep, somniphobia involves a persistent, overwhelming fear that can lead to severe sleep deprivation and related health issues. Keep reading to learn about the underlying causes, recognizable symptoms, and effective treatments that can help overcome this challenging phobia of sleeping.
- Key Takeaways
- What Is Somniphobia?
- What Causes Somniphobia?
- What Are the Symptoms of Somniphobia?
- How Do You Treat Somniphobia?
- How Can You Manage Somniphobia?
- Somniphobia FAQs
- Overcoming Somniphobia: Understanding the Fear of Sleep
Key Takeaways
- Somniphobia is a serious condition that causes intense fear and anxiety around the act of sleeping.
- The fear of sleeping can manifest through various symptoms, such as panic attacks, rapid heartbeat, and extreme anxiety.
- Professional treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy and medication, combined with lifestyle changes and proper sleep hygiene, can effectively manage somniphobia symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Self-help strategies, such as implementing consistent bedtime routines and creating a comfortable sleep environment, can complement professional treatment and support recovery.
What Is Somniphobia?
Somniphobia, also known as sleep anxiety or the phobia (fear) of sleeping, is a psychological condition characterized by an irrational fear of falling asleep.[1] The symptoms can manifest differently in those affected by them, but the core feature remains the same: an overwhelming dread of sleep that goes beyond normal bedtime anxiety. Unlike common sleep disorders, somniphobia involves a specific phobic response to the act of sleeping itself.
The condition can severely impact daily functioning, leading to sleep deprivation, excessive daytime sleepiness, and health problems. Many individuals with somniphobia find themselves trapped in a cycle where the fear of sleep creates anxiety, which in turn makes it even more difficult to achieve restful sleep. This can affect everything from work performance to personal relationships.
What Causes Somniphobia?
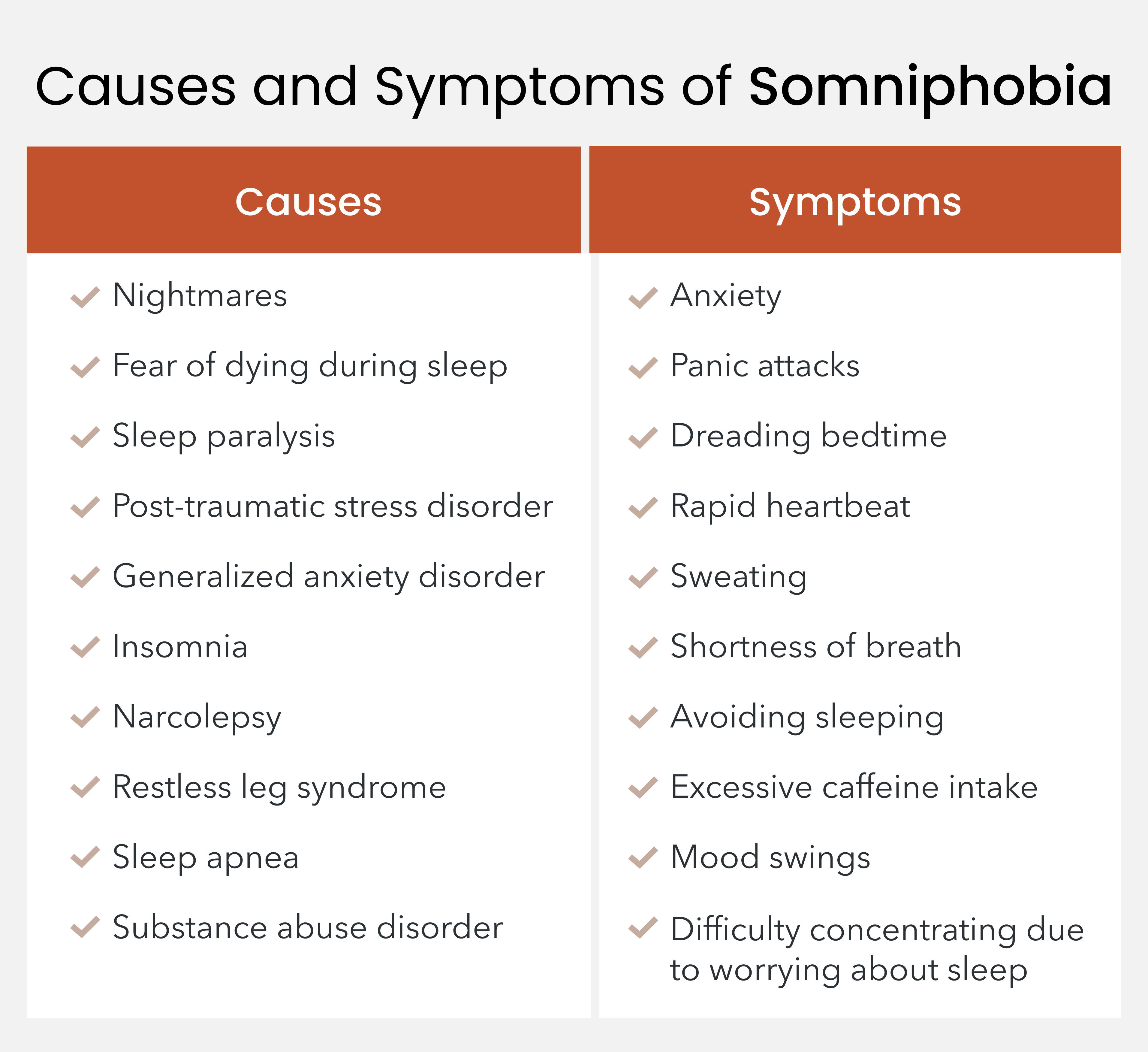
Several factors can contribute to developing this fear of sleeping, often working in combination to create and maintain the phobic response. Here are the primary causes: [1,2]
Psychological factors
Psychological factors can lead to the development and persistence of somniphobia. These underlying causes often work together to create and maintain the fear response:
- Nightmares: Frequent disturbing dreams can create intense anxiety about falling asleep, especially when they occur regularly and cause significant emotional distress. Lucid dreams, which blend a state of consciousness with dreaming, can also cause anxiety around sleeping.
- Fear of death during sleep: Some individuals develop an irrational but overwhelming fear that they might die while sleeping, often triggered by anxiety disorders or past experiences with nighttime health scares.
- Sleep paralysis: The terrifying experience of being conscious but unable to move during sleep transitions can create lasting trauma and fear of similar episodes occurring again.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder: PTSD can lead to somniphobia through trauma-related nightmares and sleep disturbances, creating a persistent fear of sleep itself.
Medical conditions
Several sleep-related medical conditions can contribute to developing somniphobia. These include:
- Insomnia: This sleep disorder refers to the inability to fall or stay asleep, which can create a negative association with bedtime. This association may increase feelings of anxiety around sleep attempts.
- Narcolepsy: This sleep disorder causes sudden sleep attacks during the day, which can trigger intense fear about losing control over when and where sleep occurs.
- Restless leg syndrome: The uncomfortable sensation and urge to move the legs is known as restless leg syndrome (RLS), which can make falling asleep a frustrating experience, contributing to sleep anxiety.
- Sleep apnea: Experiencing breathing difficulties during sleep can create legitimate fears about sleeping, particularly when episodes cause sudden awakening.
- Substance abuse disorder: The impact of drugs or alcohol on sleep patterns can trigger or worsen sleep-related anxiety, creating a cycle of dependency and fear.
What Are the Symptoms of Somniphobia?
Somniphobia can manifest through a variety of physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. People may experience different combinations of these symptoms, which can worsen as bedtime approaches. People with somniphobia may:[1]
- Experience intense anxiety or panic attacks when thinking about sleep, especially as bedtime gets closer.
- Develop physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, excessive sweating, and shortness of breath when thinking about going to bed.
- Try to stay awake as long as possible by consuming excessive caffeine or finding reasons to avoid going to bed.
- Feel increasingly anxious and restless as nighttime approaches, often experiencing a sense of dread about bedtime.
- Notice significant mood swings throughout the day, particularly when tired or thinking about sleep.
- Have trouble focusing on daily tasks because worries about sleep constantly intrude on their thoughts.
How Do You Treat Somniphobia?
Professional somniphobia treatment typically involves a combination of therapeutic approaches and, in some cases, medication. The primary treatment options are: [1,2]
- Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT): This therapeutic approach helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns about sleep. Through CBT, you can learn to develop healthier sleep-related thoughts and behaviors.
- Exposure therapy: This treatment gradually exposes individuals to sleep-related situations in a controlled, safe environment. Over time, this helps reduce the anxiety and fear responses associated with sleeping.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications such as beta blockers to manage physical symptoms or benzodiazepines for anxiety relief. Supplements, such as melatonin, might also be recommended to promote sleep. For those interested in natural options, understanding how long melatonin lasts is important when considering sleep supplements. It’s crucial to note that any medication should only be taken under direct medical supervision with a proper doctor referral.
How Can You Manage Somniphobia?
Along with professional treatment, various self-help techniques can help manage somniphobia symptoms. Using proper sleep hygiene practices and using natural sleep aids can significantly improve your sleep experience. Here are a few effective strategies to consider:

- Establish a bedtime routine: Learning how to fix your sleep schedule through consistent routines is essential for long-term improvement. Creating a consistent nightly routine signals to your body that it’s time to wind down and helps reduce anxiety around sleep. This might include activities like reading, stretching, or taking a warm bath at the same time each night.
- Use white noise to sleep: Adding white noise to your sleep environment can help mask disturbing sounds and create a consistent audio backdrop that promotes relaxation and better sleep quality.
- Try relaxation exercises: Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation for sleep, or guided imagery can help calm your mind and reduce sleep-related anxiety.
- Listen to music or podcasts: Playing relaxing playlists for sleep or listening to sleep-focused podcasts can help create a more peaceful bedtime environment.
- Use a weighted blanket: A weighted blanket may enhance comfort, potentially reducing anxiety and promoting more restful sleep. Choose a weighted blanket that’s right for you based on your weight and preferences.
- Invest in a quality bed and bedding. A comfortable mattress and supportive memory foam pillows can significantly improve your sleep experience and make bedtime more inviting.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: Reducing or eliminating caffeine and alcohol intake, especially in the house before bedtime, can help prevent sleep disruption and minimize anxiety symptoms.
- Exercise regularly: Following a consistent exercise routine during the day can help reduce general anxiety levels and promote natural tiredness at bedtime.
Somniphobia FAQs
What is the difference between somniphobia and hypnophobia?
While these terms are often used interchangeably in medical literature and clinical settings, they technically have different origins. Somniphobia comes from the Latin word “somnus,” meaning sleep, while hypnophobia derives from the Greek word “hypnos,” meaning sleep.
Both terms describe the same condition: an intense, irrational fear of sleeping. Mental health professionals may use either term when diagnosing and treating this condition, though somniphobia has become more commonly used in recent years.
How is somniphobia different from insomnia?
Though both somniphobia and insomnia can result in sleepless nights, these conditions are fundamentally different.
Insomnia is a well-known sleep disorder that refers to someone’s inability to fall or stay asleep despite wanting to do so. People with insomnia often feel frustrated because they want to sleep but can’t. In contrast, somniphobia involves an intense fear of the act of sleeping itself, where individuals actively resist sleep due to anxiety and fear.
While someone with insomnia might lie in bed trying to sleep, a person with somniphobia might avoid going to bed altogether. It’s worth noting that these conditions can coexist, with the fear of sleep potentially leading to insomnia symptoms or chronic insomnia contributing to the development of sleep-related anxiety.
When should you seek professional help for somniphobia?
Professional help for somniphobia should be sought when the fear of sleep begins to significantly impact your daily life and overall well-being. Indications it’s time to consult a mental health professional or sleep specialist include:
- Your fear of sleep persists for more than two weeks and isn’t improving with self-help strategies.
- The anxiety about sleeping is severe enough to cause nocturnal panic attacks or extreme distress.
- You’ve developed potentially dangerous coping mechanisms, such as excessive caffeine consumption or self-medication.
- Your sleep avoidance is affecting your work performance, relationships, or daily activities.
- You’re experiencing physical symptoms like persistent fatigue, headaches, or difficulty concentrating.
Remember that seeking help early can prevent the condition from becoming more severe and improve your chances of successful treatment.
Overcoming Somniphobia: Understanding the Fear of Sleep
Somniphobia is a complex intersection of anxiety, fear, and sleep disruption that can significantly impact quality of life. Professional treatment, lifestyle changes, and consistent self-help strategies can help people work toward overcoming their fear of sleep and establishing healthier sleep patterns.
At Layla, we understand the importance of creating the perfect sleep environment for managing sleep-related anxieties. Our collection of sleep products, from premium memory foam mattresses to weighted blankets, is designed to provide the comfort and support needed for a peaceful night’s rest. Browse our products to discover our full range of sleep solutions and take the first step toward better sleep.
References
- “Somniphobia (Fear of Sleep): Causes, Symptoms & Treatment.” Cleveland Clinic, 24 Jan. 2025, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22645-somniphobia.
- “Somniphobia: Understanding the Fear of Sleep.” Sleep Foundation, 3 May 2024, www.sleepfoundation.org/mental-health/somniphobia.



